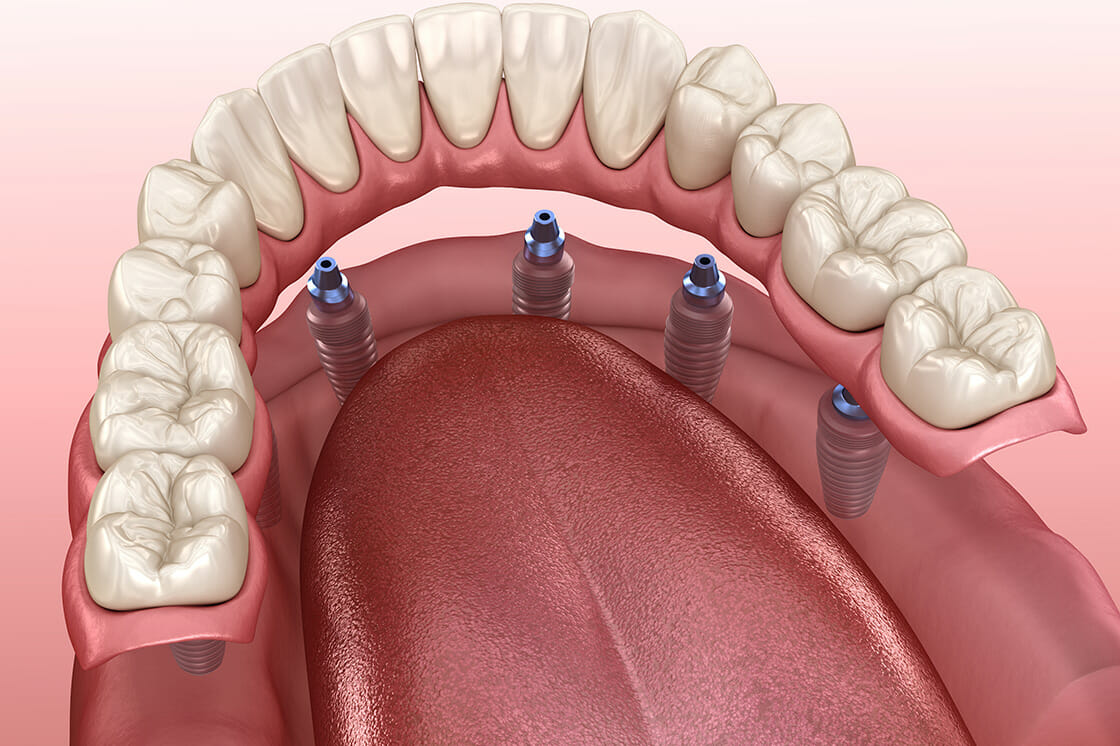
Regular dentures sit on top of your gums and use the tissue of your mouth to support themselves. Though this is an option to replace a full mouth of teeth, there are other options, like implant-supported dentures, which snap into dental implants, providing a firm fit.
What are the benefits of Implant-Supported Dentures?
Implant-supported dentures use “snap” dental implants to support them, as opposed to the soft and hard tissues of your jaw and mouth. This allows for a tight and supportive fit, as well as getting rid of the need for dental adhesives often used with traditional dentures. These types of dentures are still removable though. They snap onto posts that are implanted directly into your jaw, meaning you can remove the dentures to clean them and to clean your mouth. This type of denture is often used on the lower jaw since the implants need a strong bone to support them. Other benefits include:
- Improved confidence,
- Stability during eating,
- Bone and gum preservation,
- Improved dental hygiene,
- Superior esthetics, and
- Nutritional benefits.
What types of Implant Supported Dentures are there and what’s the difference?
Two types of Implant-Supported Dentures exist — bar-retained dentures and ball-retained dentures. In bar-retained dentures, three or more dental implants are placed into the jaw bone, and a metal bar runs along the gum line between each implant. The dentures attach to the bar using metal clips, and this secures the dentures to your jaw. This option typically relieves the patient of rubbing, loosening, or discomfort associated with traditional dentures. On the other hand, ball-retained dentures use a ball and socket mechanism to lock into the dentures. The base for the dentures has several sockets that line up with balls placed on dental implants in the jaw bone. These balls and sockets fit together securely. In comparison with other types of dentures, the ball-retained dentures are the least likely to slip or move, allowing the patient to eat, speak, and go about their daily life regularly.
If either of these options sounds like a good fit for you, please contact Dr. Mays’ office to make an appointment at 513-321-1102 or janemaysdmd@gmail.com.